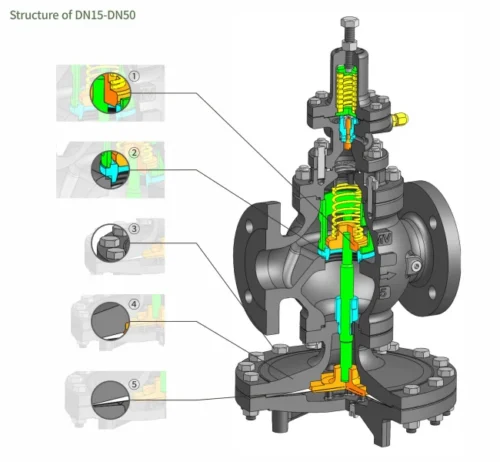
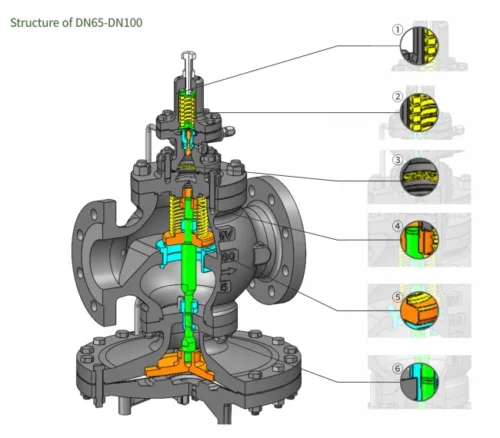
Description
In the steam system of heating, temperature control, refrigeration and even the entire field of industrial fluid automation, the pressure reducing valve is a common and indispensable fluid control component. Its main function is to reduce the high-pressure steam to the low-pressure steam required by the equipment to ensure that the equipment is in the most efficient working state. These valves operate without requiring any external power source or controller, utilizing the steam medium itself as the motive force to automatically adjust and stabilize the pressure downstream of the valve.
Conventional pressure reducing valves often suffer from issues such as poor regulation accuracy, significant pressure fluctuations after reduction, short service life, and excesive leakage. In severe cases, they can even cause downstream over pressure, leading to emergency shutdowns and substantial losses for users.
To address this series of risks, VMV Newton’s R&D team conducted in.depth on-site investigations, gathered extensive operational data, and undertook significant technicall development, Through rigorous testing and validation, we designed, manufactured, and have successfully delivered the V5001 series pilot-operated reducing valve, which fully meet user requirements.
The V5001 series pilot-operated pressure reducing valve offers the following features:
- High pressure reduction accuracy: 士3%
- Wide pressure adjustment range: 0.02-2MPa
- Large pressure reduction ratio: 20:1
- Good control stability
- Long service life
- High temperature and pressure resistance
- Large flow capacity
- Fast response speed

Working Principle
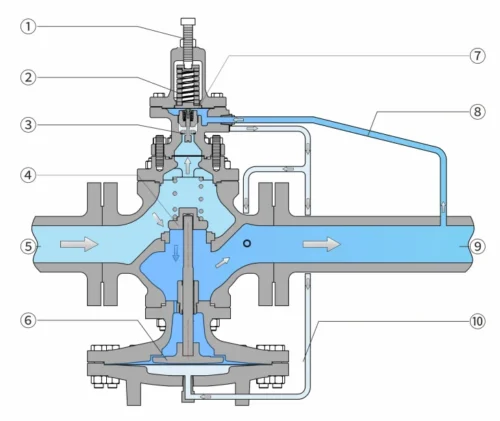
| Item | Name |
| 1 | Pressure regulation |
| 2 | Control spring |
| 3 | Pilot valve core and valve seat |
| 4 | Main valve core and valve seat |
| 5 | High pressure steam inlet |
| 6 | Main valve diaphragm |
| 7 | Pilot diaphragm |
| 8 | Downstream pressure sensing line |
| 9 | Low pressure steam outlet |
| 10 | Control pressure |
- The main valve is normally closed, and the pilot valve is normally open. When the regulatingvalve is put into operation, the steam enters the inner cavity of the pilot valve through the pilotvalve core and the valve seat;
- The steam is divided into two paths after the pilot inner cavity,one path is connected to the valve to release the steam pressure; the other path enters the main valve diaphragm, generating pressure to push the main valve core to open; the steam enters the rear pipeline from the main valve core and the valve seat; as the rear steam outlet pressure increases,it overcomes the force added by the control spring and the pilot valve core throtling, so that the main valve core is at an appropriate throttling opening, thereby maintaining the outlet pressure at the set value;
- When the downstream pressure increases, the pilot valve core is closed, and the pressure is released from the main valve diaphragm through the control hole, thereby closing the main valve. Any changes in load or presure will e immediately sensed by the pilot diaphragm, and the position of the main valve willbe adjusted accordingly to ensure that the downstream pressure is constant.
Typical Installation Diagram Example
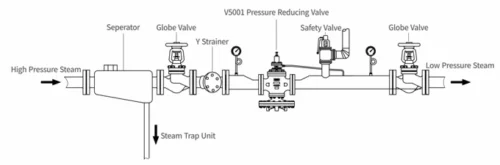
1.The standard-installed pressure reduction system
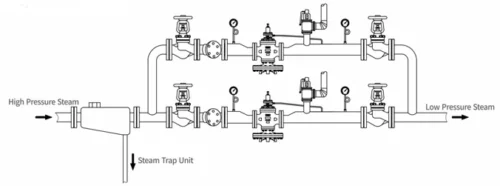
2.Parallel-installed pressure reduction system: used for large flow variations or backupoperating conditions
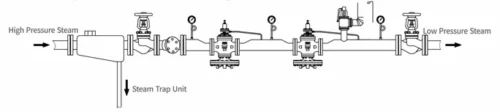
3.Series-connected pressure reduction system, used for high-pressure pressure reductionscenarios (pressure reduction ratio > 10:1)
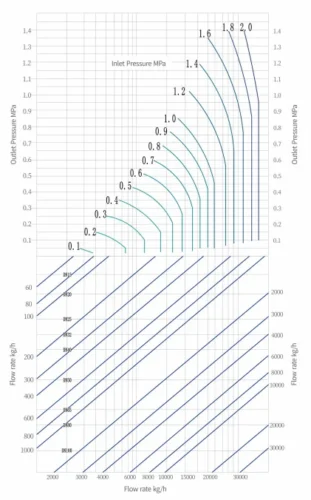
Rated Cv Value
| Size | DN15 | DN20 | DN25 | DN32 | DN40 | DN50 | DN65 | DN80 | DN100 |
| Rated Cv | 5 | 7 | 11 | 14 | 20 | 35 | 54 | 70 | 108 |